Nanorobot: The Future of Medical Science
— Mahnoor Patel. Department of Biotechnology, Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, Surat, Gujarat, India. 2019.
Abstract
“Nanorobotics is the branch of nanotechnology. Nanorobotics is important in creating machines or robots which is close to the microscopic scale of nanometer (10-9 m). A nanorobot is a tiny machine and it is designed specifically to perform a specific or particular task repeatedly and with great precision at nanoscale dimensions. The diameter of nanorobot is about 0.5 to 3 microns and it is constructed out of parts which have dimension range of 1 to 100 nm. Nanorobotics has strong potential to revolutionized healthcare, to treat disease in future. Nanotechnology changes the shape of industry, broadening the product development and interrelationship between pharmaceuticals, biotechnology and healthcare industry. Nanorobots are used for various purposes in medical science.
Elements of Nanorobots
Carbon is the principle element of nanorobot used in medical science. With this hydrogen, fluorine, sulfur, oxygen, nitrogen and silicon can be use.
Injection of Nanorobots into the Body
The size of the nanorobot is determined by the size of the blood vessel that it can transverse. Because the cell wall cannot be damaged or cannot be blocked by the medicine which is injected into it.
The nanorobot can be injected without damaging at the first place of insertion. That’s why the first large diameter artery can be selected for the insertion, which can be able to gain access in a very short time duration into the whole body. The femoral artery of the leg can be selected for this purpose.
Ways of Tracking
Tracking and controlling nanobots include such means as: Ultrasound, MMR/MRI, radioactive dye, X-rays, using special chemicals, spectroscope, TV cameras. Nanobots are going to play very important role in the future medical science. They can even start a revolution in medicine. However, there are some disadvantages which accompany the use of nanorobots. The complexity of the design and manufacture, accompanied by high cost, is a major drawback for the wide application of nanorobots. Nanorobots can be tracked by many different ways.”
Nanobots For Medicinal Applications
— Smrutimedha Parida & Anil Ramdas Bari. Journal of Nanomedicine & Nanotechnology, Vol, 11, Issue 1 (2023).
[See Notes In PDF File]
Abstract
“The applications of nanotechnology have increased exponentially in the field of medicinal chemistry with the implementations of nanorobotics. Nanobots provide one of the most promising areas of nanotechnology spreading its roots to applications in various fields including medical imaging, drug delivery and even in the development of Nanobots have the advantages of small size, low weight, large thrust-to-weight ratio, high flexibility, and high sensitivity. The applications of nanobots are varied and are being explored in various fields. The aim of this review is to offer an overview to the emerging field of nanorobotics within medicinal chemistry and their applications for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of various diseases. It provides a comprehensive overview of the development of nanobots. The key components of the robots and the types of nanobots are discussed separately. The review also focuses on the disadvantages and the challenges in the development of nanobots for their specific causes. And finally, the efforts and measures that can bring us steps closer to the dream of catching up with our fantasies of developing tiny robots that could roam about inside our bodies, delivering drugs with unprecedented precision, and hunting down and destroying infected cells and most importantly science fiction becoming scientific fact are discussed.
Keywords: Nanomedicine; Nanobot; Nanomotors; Sensors; DNA nanorobot; Targeted drug delivery; Precision surgery.” (p. 1)
“Nanocomputers: They can be electronic, biochemical, organic or quantum and have the function of controlling or directing nanobots inside the body. Computers developed at a molecular level made up of DNA, having software coded with four letters of DNA nitrogenous bases can regulate gene expression. It can also detect the type of mRNA associated with specific genes that in case of being over expressed or its opposite induce the cancer. This allows diagnosing different types of cancer and counteracting the disease with the indicated drug [24].
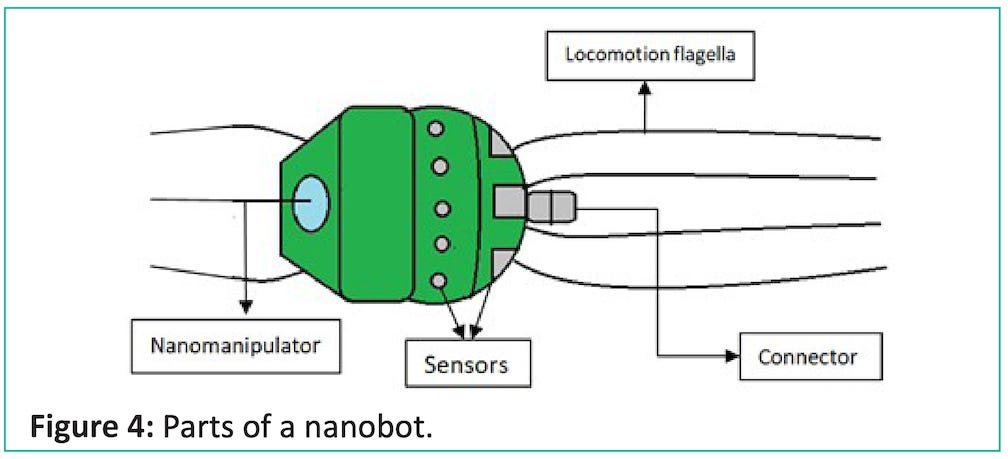
The nanobot design consists of integrated nano electronics and components. Binding sites of different sensors have a different affinity for distinct molecule types. Sensors detect obstacles which require a new trajectory planning and their design depends on the environment and the task. A nanobot needs transducers capabilities and smart sensors directly related to specific biomedical application. It relies on chemical contact sensors to detect them. Different nanobot sensor based actions can be evaluated by this interaction capabilities [25]. By this, we can choose the kind of low-level control to maximize the information acquired for an effective real time performance. The nanobot kinematics can be predicted using state equations, positional constraints, inverse kinematics and dynamics, while some individual directional component performance can be simulated using control system models of transient and steady state response [26]. The capacity to design, build, and deploy large numbers of medical nanobots into the human body would make possible the rapid elimination of disease and the effective and relatively painless recovery from physical trauma.
Types of nanobots: Generally nanobots can be classified into two types i.e. organic also called bionanobot and inorganic nanobots.
Nanobots in drug delivery and therapeutics can also be classified according to the applications as described below:
Pharmacyte: It is a medical nanobot used to carry a given drug in the tanks. It is controlled using mechanical systems for sorting pumps. For full targeting accuracy, it has molecular markers or chemotactic sensors. Glucose and oxygen that are extracted from the local environments such as blood, intestinal fluid and cytosol are the on board power supply. Nanobots are removed after completing their tasks by centrifuge nanapheresis [29].
Diagnosis and Imaging nanobots: These nanobots have microchips projected to send electrical signals when the human molecules on the chips detect a disease. They can also be used to monitor the sugar level in the blood. Their production cost is and they can be easily manipulated [27].
Respirocyte: It is Artificial Oxygen Carrier nanobot. Its power is obtained by endogenous serum glucose. This artificial cell is able to give 236 times more oxygen to the tissues per unit volume than RBCs (Red blood cells). It is also used to administer acidity [28].
Microbivores: It is an oblate spheroidal device for nanomedical applications. The nanobot can continually consume power up to 200pW and this power is used to digest trapped microbes. It also has the ability to phagocyte approximately 80 times more efficiently than macrophages agents, in terms of volume/sec digested per unit volume of phagocytic agent [29].
Clottocytes: This nanobot has the ability for instant hemostasis. They are also called artificial mechanical platelets that are roughly spheroidal nucleus-free blood cells. Platelets join at a place of bleeding and are activated. Then they aid in stamping the blood vessel and stop the bleeding. They also deliver substances that help promote coagulation[28].
Chromallocyte: They replace entire chromosomes in individual cells thus reversing the effects of genetic disease and other accumulated damage to our genes, preventing aging. Usually inside a cell, first the repair machine sizes up the situation by examining the cell’s contents and activity, and then takes action by working along molecule-by-molecule and structure-by structure [29].
DNA nanobots: They are used to deliver the drug to the targeted cell so as to avoid side effects. […] DNA nanobots are used as a targeted drug delivery system to improve treatment of diseases [64].” (pp. 2-3)
Challenges for Handling of Nanobots
“Though nanobots have unrivalled advantages due to their size, they also face some challenges. When the dimensions are reduced to nano scale, the nature of certain physical laws is altered due to changes in the surface area-to-volume ratio and surface area. Perimeter-related forces tend to predominate. The behavior of nanobots is also relatively susceptible to temperature, humidity, and fluids.” (p. 5)
[See Notes In PDF]